|
1 | | ---- |
2 | | -comments: true |
3 | | ---- |
| 1 | +The Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK) is an open-source stack to build layer 2 blockchains powered by zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs. |
4 | 2 |
|
5 | | -Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK) is a modular, open source software toolkit for blockchain developers which supports the installation and configuration of a variety of chain architectures. Polygon CDK empowers developers to launch new L2 chains running Polygon zkEVM technology on Ethereum or, in the future, transition existing Layer 1 (L1) chains into ZK-EVM L2s. |
| 3 | +It consists of several modular components, many of which are used to power the Polygon zkEVM in production today, that are designed to be fully composable; empowering developers to customize each component and build a chain that meets their specific needs. |
6 | 4 |
|
7 | | -!!! warning "ZK-EVM versus zkEVM - term usage" |
8 | | - - **ZK-EVM**: The capitalized and hyphenated usage of the term refers to any zero-knowledge rollup chain in general. |
9 | | - - **zkEVM** refers to Polygon's zero-knowledge rollup and validium scaling solution. |
| 5 | +## Why Build With the CDK? |
10 | 6 |
|
11 | | -## CDK options |
| 7 | +The CDK bootstraps the development process of creating a layer 2 blockchain. Developers can easily set up the stack and begin configuring each component’s behavior with a fast feedback loop on a local development environment. |
12 | 8 |
|
13 | | -With Polygon CDK, developers can select a chain architecture specific to their needs from a set of supported, open source components. Alternatively, developers can select custom components for specific requirements. The diagram below shows the two supported configuration options, zkEVM rollup or validium. zkEVM rollups post transaction data from Polygon CDK directly onto Ethereum, whereas validiums only post the transaction hashes, while storing transaction data off-chain. |
| 9 | +As logic is separated into modular components, developers can easily swap out components in a "plug and play" fashion to customize their chain, for example, by replacing entire components such as the data availability layer, or making granular-level configurations to each component; such as modifying the sequencer logic to comply with legal regulations. |
14 | 10 |
|
15 | | - |
| 11 | +### Tap Into the AggLayer |
16 | 12 |
|
17 | | -A chain tailored for a specific application might leverage the zkEVM execution environment, adopt the validium mode, and implement a centralized sequencer. |
| 13 | +By default, CDK chains are opted into the Aggregation Layer (AggLayer) which enables cross-chain transactions among other L2 chains that are also opted into the AggLayer including the Polygon zkEVM. |
18 | 14 |
|
19 | | -!!! note "Example use case" |
20 | | - A CDK zkEVM rollup L2 chain dedicated to running a game has lower security requirements than a high-value DeFi application. This could also use a validium mode for off-chain data availability to further reduce transaction costs. |
| 15 | +This provides a powerful network effect by enabling users to interact with smart contracts on your chain without having to manually bridge assets to it. This is especially useful for developers looking to bootstrap their chain’s ecosystem and have immediate access to a large pool of users and liquidity. |
21 | 16 |
|
22 | | -!!! info "Coming soon" |
23 | | - Upon the completion of the aggregation layer, every chain will have the option to be interoperable with other Polygon network chains. For now, the aggregation layer in the CDK kit allows for independent chains (1-to-1) to settle independently. |
| 17 | +### Utilize Best-in-Class ZK Technology |
24 | 18 |
|
25 | | -## Sovereign and modular chain design |
| 19 | +The Polygon team are pioneers in the zero-knowledge ecosystem and has built many of the most advanced ZK technologies in production today such as plonky2 and plonky3. |
26 | 20 |
|
27 | | -Polygon CDK gives developers a toolkit for sovereign and modular chain design, without sacrificing future interoperability with other L2 chains. Chains built with Polygon CDK can access an ecosystem of (forthcoming) unified liquidity, optimized performance, and seamless asset transfers, all while prioritizing user experience and data security. |
| 21 | +The CDK leverages these technologies to provide a high-performance, scalable, and secure layer 2 blockchain that is battle-tested in production with the Polygon zkEVM. |
28 | 22 |
|
29 | | -## CDK features |
| 23 | +## Dive Deeper into the CDK |
30 | 24 |
|
31 | | -Here is what developers can expect when they build with Polygon CDK. |
| 25 | +Whether you’re a developer looking to build a new chain or a researcher interested in looking under the hood, the CDK documentation provides a comprehensive guide to the CDK’s architecture, components, and how to get started building with the CDK: |
32 | 26 |
|
33 | | -1. **Modularity and sovereignty**: Polygon CDK offers a modular environment for ZK-powered L2 chain design. Developers can customize chains according to their needs. |
34 | | -2. **Scalability**: Polygon CDK-developed L2 chains enhance transaction speed and can be multiplied to achieve an elastically scalable ecosystem. |
35 | | -3. **Independent data availability**: With a dedicated data availability layer and a data availability committee, Polygon CDK-developed chains provide robust off-chain data access and reliability. This structure, independent of Ethereum, ensures substantial data resilience and integrity. |
36 | | -4. **Interoperability (forthcoming)**: Through an in-development interop layer, CDK-developed chains can be seamlessly interoperable, meaning atomic L2 <> L2 transactions. Chains deployed with Polygon CDK will have the opportunity to opt-in to the interop layer and tap unified liquidity. |
37 | | -5. **Near-instant finality**: Chains deployed using Polygon CDK rely on cryptographic security, ensuring transaction integrity without the need of full nodes. This approach guarantees near-instant finality and robust security. |
38 | | -6. **Extensive Web3 support**: Polygon CDK chains leverage a comprehensive ecosystem with premium service providers offering essential tools for application integration, development, and deployment. |
39 | | - |
40 | | -!!! important "Why are there zkEVM docs in the CDK section?" |
41 | | - Several of the docs point to zkEVM specific deployment documentation because the rollup flavor of CDK uses zkEVM deployment defaults. |
42 | | - |
43 | | -The following diagram illustrates how Polygon CDK-developed chains may opt into a web of interoperable L2 chains: |
44 | | - |
45 | | -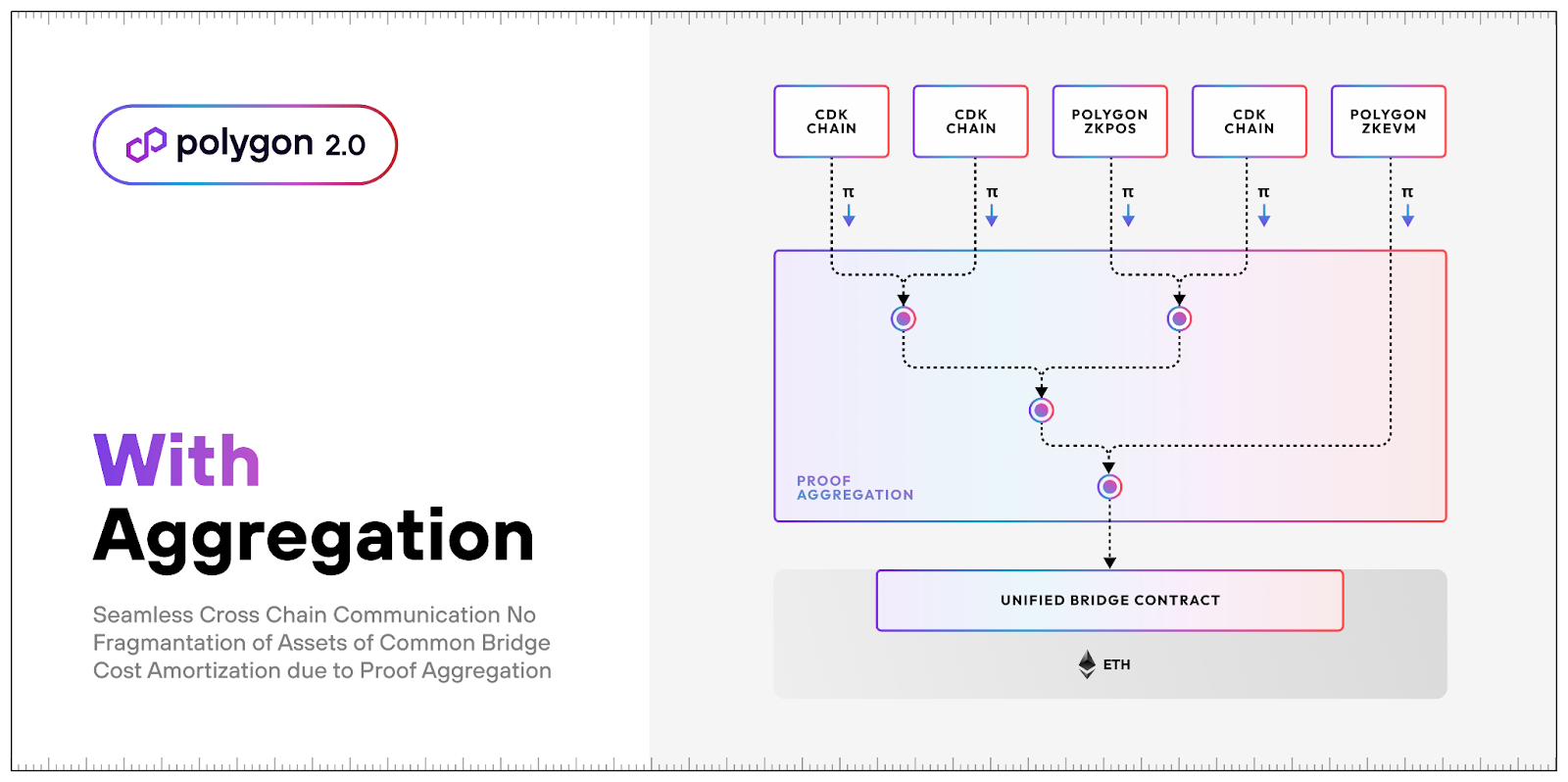 |
| 27 | +- concepts behind the CDK and how it works. |
| 28 | +- todo |
| 29 | +- todo |
0 commit comments